Sunday, July 11, 2021
Performance Parameters of The I.C. Engine PPT, Definition, Working
Engine performance is an indication of the degree of success with which it converts the chemical energy of fuel into useful mechanical work. To evaluate the performance of 1.C. engines certain basic parameters are chosen and the effect of various operating conditions, design concepts and modifications on these parameters are studied.
The total power developed by the combustion of fuel in the combustion chamber is called indicated power (1.P.)
Where,
Pim = Indicated mean effective pressure, bar
L= Length of stroke, m
A = Area of piston, m²
n = Number of working strokes per minute,
=N, for two-stroke engine
N = Engine speed, r.p.m,
K = Number of cylinders,
Brake Power The power developed by an engine at the output of the shaft is called as brake power (B.P.)
Where,
T = Engine torque, N-m.
The brake power of an engine is measured by measuring the torque and angular speed of the engine output shaft. The device used for torque measurement is called a dynamometer. A dynamometer is essentially a brake, in which an additional device has been incorporated for measuring the frictional resistance.
Dynamometers can be classified into the following two types -
(i) Absorption dynamometers.
(ii) Transmission dynamometers.
Mean effective pressure (M.E.P) is the hypothetical pressure that is thought to be acting on the piston throughout the power stroke.
Since power generated by an engine depends upon its size and speed, therefore engines cannot be compared on the basis of power. While m.e.p. can be considered as a true indicator of the relative performance of different engines.
When m.e.p. is calculated on the basis of indicated power, it is called indicated mean effective pressure (Pim) and when it is calculated on the basis of brake power it is called brake mean effective pressure (Pbm).
Indicated thermal efficiency is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent of power produced in the cylinder in-unit o time and heat supplied to the engine in unit time.
Where,
Mf = Fuel oil supplied in kg per sec,
CV = Calorific value of fuel in kJ/kg,
Brake thermal efficiency is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent of brake power in unit time and heat supplied to the engine in unit time.
Mechanical efficiency may be defined as the ratio of useful power available at the engine crankshaft and power developed in the engine cylinder.
Relative Efficiency is also called the efficiency ratio. The relative ere engine efficiency is defined as the ratio of indicated thermal efficiency to the air standard efficiency.
(ix) Specific fuel consumption,
(x) Specific power output.
Tags
# internalcombustionengine
![Author Image]()
About Dangerous Biography
Soratemplates is a blogger resources site is a provider of high quality blogger template with premium looking layout and robust design. The main mission of soratemplates is to provide the best quality blogger templates which are professionally designed and perfectlly seo optimized to deliver best result for your blog.
internalcombustionengine
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)








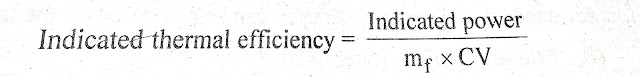








No comments:
Post a Comment